Unrefined data serves no practical purpose. Its untapped potential gains purpose and direction only when shaped by prescriptive and
predictive analytics. The ability to analyse, interpret, and act on vast amounts of data has become a critical differentiator. Understanding the differences between
predictive vs prescriptive analytics and their applications is essential for businesses aiming to optimise performance, reduce risks, and maximise growth. With a forecasted CAGR of 19.6% from 2017 to 2026, the predictive and prescriptive analytics market is set to grow to $28.7 billion.
In this blog, we’ll explore how predictive and prescriptive analytics empower organisations to turn data into actionable insights.
Predictive analytics interprets historical data and machine learning models to forecast future trends that can impact business processes. This aids businesses in anticipating customer behaviour, market shifts, and operational needs. Predictive analytics generally deals with large and complex datasets for building statistical models, as well as identifying and interpreting patterns and trends.
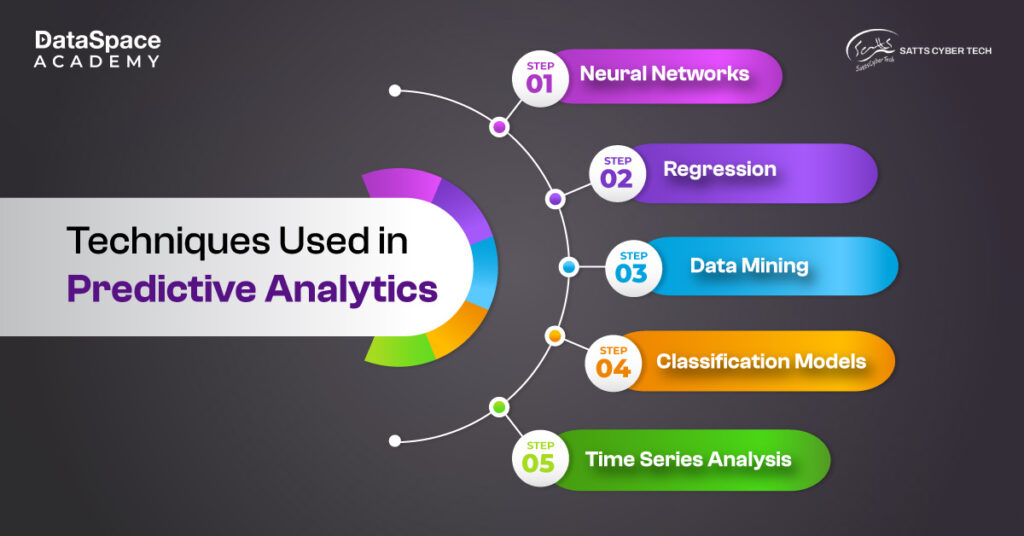
Simply put, predictive analytics results are prediction-oriented and don’t recommend actions. Let’s say, every business maintains financial records. Now, by using predictive analytics, businesses are able to get an estimated insight into their financial future and plan accordingly. Some of the key
predictive analytics techniques include time series forecasting, decision tree structures, and regression analysis.
Prescriptive analytics takes the analytics game a step further. It not only predicts outcomes but also recommends actionable strategies to achieve desired results. This form of analytics suggests optimal actions by analysing data, predictions, and constraints.
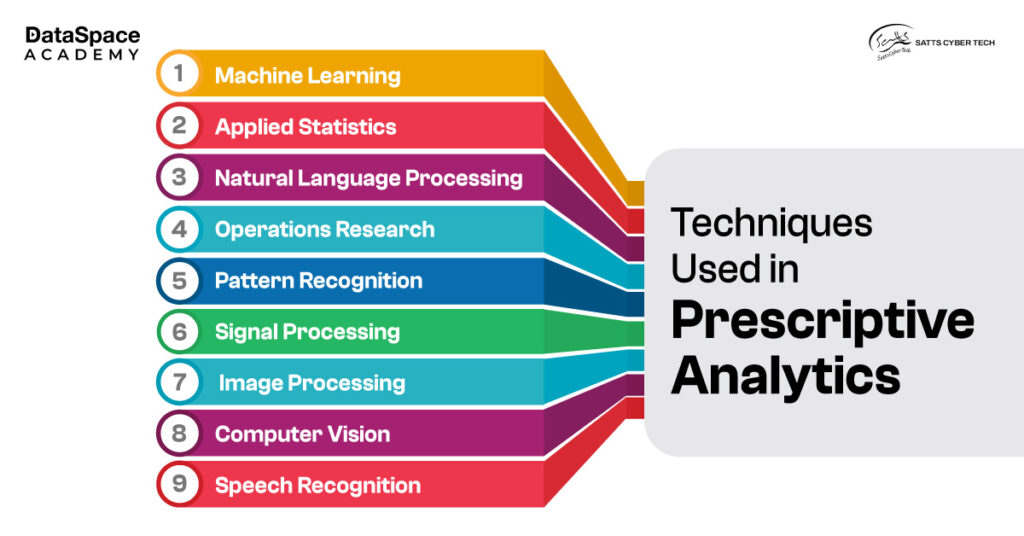
Here we present a simple comparative breakdown of these two analytical methodologies for better and clear understanding of the concepts.
| Predictive Analytics | Prescriptive Analytics |
|---|
| 1. Theme: What will happen? | 1. Theme: How to make it happen? |
| 2. Forecasts future outcomes based on historical data and patterns | 2. Recommends the best course of action by analysing potential outcomes |
| 3. Relies on statistical models, machine learning, and algorithms | 3. Builds on predictive insights |
| 4. Complexity level: Low | 4. Complexity level: High |
| 5. A decision support method | 5. A decision making method |
| 6. Methods used: time series analysis, decision trees, and regression analysis | 6. Methods used: optimisation techniques, simulation, game theory, and so on |
| 7. Predictive analytics tools: KNIME, RapidMiner, Tableau, and Apache Spark | 7. Prescriptive analytics tools: Alteryx, Microsoft Azure Machine, and Improvado |
This analytical approach is all about interpreting historical data to predict future outcomes. Here are some of the real-world applications of predictive analytics.
This approach not only predicts what could happen but also suggests actions for fruitful outcomes. Here are a few majo use cases of Prescriptive Analytics.
As big data is becoming the driving factor in identifying risks and opportunities, the importance of predictive and prescriptive analytics will remain significant. It’s time to level-up your analytical skills by enrolling in DataSpace Academy’s industry-leading
data analytics certification course.

 Simply put, predictive analytics results are prediction-oriented and don’t recommend actions. Let’s say, every business maintains financial records. Now, by using predictive analytics, businesses are able to get an estimated insight into their financial future and plan accordingly. Some of the key predictive analytics techniques include time series forecasting, decision tree structures, and regression analysis.
Simply put, predictive analytics results are prediction-oriented and don’t recommend actions. Let’s say, every business maintains financial records. Now, by using predictive analytics, businesses are able to get an estimated insight into their financial future and plan accordingly. Some of the key predictive analytics techniques include time series forecasting, decision tree structures, and regression analysis.

